The Leadership Styles are the behavioral patterns that a leader adopt to influence the behavior of his followers, i.e. the way he gives directions to his subordinates and motivates them to accomplish the given objectives.
The leadership styles can either be classified on the basis of behavioral approach or situational approach. These approaches are comprised of several theories and models which are explained below:
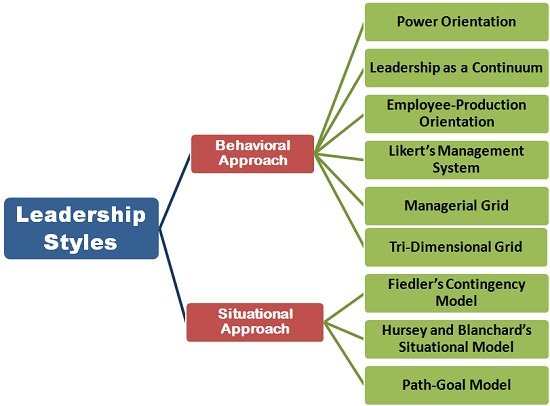
Based on Behavioral Approach
- Power Orientation
The power orientation refers to the “degree of authority” that a leader adopts to influence the behavior of his subordinates. Based on this, the leadership styles can be further classified as:
- Autocratic Leadership
- Participative Leadership
- Laissez-Faire
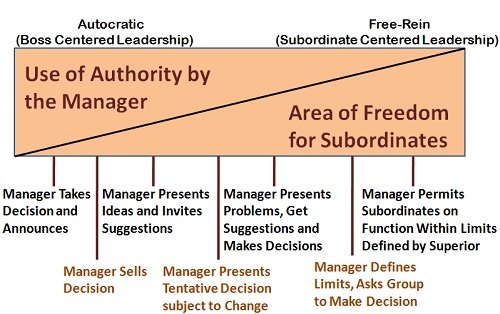
- Leadership as a continuum
This model is given by Tannenbaum and Schmidt, who believed that there are several leadership styles that range between two extremes of autocratic and free-rein, which are shown below:
- Employee-Production Orientation
Several types of research were conducted to study the leadership behavior that gets affected by the several characteristics that are related to each other. It was found that employee orientation and production orientation play an important role in determining the leadership style. The employee orientation is based on the premise that an employee is an important part of the group and is in parallel to the democratic leadership style. Whereas the production Orientation focuses on the production and technical aspects of the job and the employees are considered as the tools for accomplishing the jobs. Thus, the production orientation is parallel to the autocratic leadership style.
- Likert’s Management System
Rensis Likert along with his associates studied the patterns and behavior of managers to identify the leadership styles and defined four systems of management. These four systems are: Exploitative Authoritative, Benevolent Authoritative, consultative system and participative system.
- Managerial Grid
The managerial grid is the tool designed by Blake and Mouton to determine the leadership style. According to them, the leadership style gets influenced by both the task-oriented and relation-oriented behavior in varying degrees.
- Three Dimensional Grid
The three-dimensional grid is also called as a 3-D leadership model given by W.J. Reddin. Reddin included the effectiveness dimension along with the task-oriented and relationship-oriented dimensions to study how a leader behaves in a given situation and a specific environment.
Based on Situational Approach
- Fiedler’s Contingency Model
This theory is given by Fred Fiedler, who, along with his associates identified the situational variables and their relationship to determine the leadership styles. Thus, this model is comprised of three elements, leadership styles, situational variables and the interrelationship between these two.
- Hursey and Blanchard’s Situational Model
According to this model, the leader has to adopt the leadership style that matches up with the subordinate’s maturity i.e. his willingness to direct his behavior towards the goal.
- Path-Goal Model
The Path-Goal Model is given by Robert House, who, along with his associates tried to predict the effectiveness of leadership styles in varied situations. He believed that the foremost function of any leader is to define the goals to the subordinates clearly and assist them in finding the best path to accomplish that goal.