A decision support system (DSS) is a computerized program used to support determinations, judgments, and courses of action in an organization or a business. A DSS sifts through and analyzes massive amounts of data, compiling comprehensive information that can be used to solve problems and in decision-making.
Typical information used by a DSS includes target or projected revenue, sales figures or past ones from different time periods, and other inventory- or operations-related data.
A DSS can be used by operations management and planning levels in an organization to compile information and data and synthesize it into actionable intelligence. This allows the end user to make more informed decisions at a quicker pace.
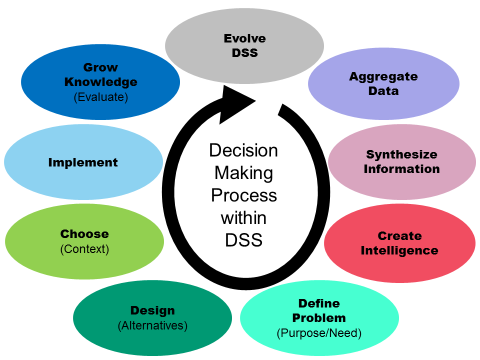
The DSS is an information application that produces comprehensive information. This is different from an operations application, which would be used to collect the data in the first place. A DSS is primarily used by mid- to upper-level management, and it is key for understanding large amounts of data.
For example, a DSS could be used to project a company’s revenue over the upcoming six months based on new assumptions about product sales. Due to the large amount of variables that surround the projected revenue figures, this is not a straightforward calculation that can be done by hand. A DSS can integrate multiple variables and generate an outcome and alternate outcomes, all based on the company’s past product sales data and current variables.
The primary purpose of using a DSS is to present information to the customer in a way that is easy to understand. A DSS system is beneficial because it can be programed to generate many types of reports, all based on user specifications. A DSS can generate information and output it graphically, such as a bar chart that represents projected revenue, or as a written report.
As technology continues to advance, data analysis is no longer limited to large bulky mainframes. Since a DSS is essentially an application, it can be loaded on most computer systems, including laptops. Certain DSS applications are also available through mobile devices. The flexibility of the DSS is extremely beneficial for customers who travel frequently. This gives them the opportunity to be well-informed at all times, which in turn provides them with the ability to make the best decisions for their company and customers at any time.
Attributes of a DSS
- Adaptability and flexibility
- High level of Interactivity
- Ease of use
- Efficiency and effectiveness
- Complete control by decision-makers
- Ease of development
- Extendibility
- Support for modeling and analysis
- Support for data access
- Standalone, integrated, and Web-based
Characteristics of a DSS
- Support for decision-makers in semi-structured and unstructured problems.
- Support for managers at various managerial levels, ranging from top executive to line managers.
- Support for individuals and groups. Less structured problems often requires the involvement of several individuals from different departments and organization level.
- Support for interdependent or sequential decisions.
- Support for intelligence, design, choice, and implementation.
- Support for variety of decision processes and styles.
- DSSs are adaptive over time.
Benefits of DSS
- Improves efficiency and speed of decision-making activities.
- Increases the control, competitiveness and capability of futuristic decision-making of the organization.
- Facilitates interpersonal communication.
- Encourages learning or training.
- Since it is mostly used in non-programmed decisions, it reveals new approaches and sets up new evidences for an unusual decision.
- Helps automate managerial processes.
Components of a DSS
(i) Database Management System (DBMS)
To solve a problem the necessary data may come from internal or external database. In an organization, internal data are generated by a system such as TPS and MIS. External data come from a variety of sources such as newspapers, online data services, databases (financial, marketing, human resources).
(ii) Model Management System
It stores and accesses models that managers use to make decisions. Such models are used for designing manufacturing facility, analyzing the financial health of an organization, forecasting demand of a product or service, etc.
(iii) Support Tools
Support tools like online help; pulls down menus, user interfaces, graphical analysis, error correction mechanism, facilitates the user interactions with the system.
Classification of DSS
There are several ways to classify DSS. Hoi Apple and Whinstone classifies DSS as follows:
(i) Text Oriented DSS
It contains textually represented information that could have a bearing on decision. It allows documents to be electronically created, revised and viewed as needed.
(ii) Database Oriented DSS
Database plays a major role here; it contains organized and highly structured data.
(iii) Spreadsheet Oriented DSS
It contains information in spread sheets that allows create, view, modify procedural knowledge and also instructs the system to execute self-contained instructions. The most popular tool is Excel and Lotus 1-2-3.
(iv) Solver Oriented DSS
It is based on a solver, which is an algorithm or procedure written for performing certain calculations and particular program type.
(v) Rules Oriented DSS
It follows certain procedures adopted as rules.
(vi) Rules Oriented DSS
Procedures are adopted in rules oriented DSS. Export system is the example.
(vii) Compound DSS
It is built by using two or more of the five structures explained above.
Types of DSS
(i) Status Inquiry System
It helps in taking operational, management level, or middle level management decisions, for example daily schedules of jobs to machines or machines to operators.
(ii) Data Analysis System
It needs comparative analysis and makes use of formula or an algorithm, for example cash flow analysis, inventory analysis etc.
(iii) Information Analysis System
In this system data is analyzed and the information report is generated. For example, sales analysis, accounts receivable systems, market analysis etc.
(iv) Accounting System
It keeps track of accounting and finance related information, for example, final account, accounts receivables, accounts payables, etc. that keep track of the major aspects of the business.
(v) Model Based System
Simulation models or optimization models used for decision-making are used infrequently and creates general guidelines for operation or management.